Understanding the MID Function: A Simple Analogy
Ever needed to pull specific pieces of text from your Excel spreadsheets? The MID function is your solution! It's like having a precise pair of scissors for your data, letting you extract exactly what you need. This guide will show you how to use it effectively, from basic techniques to advanced applications.
Imagine you have the sentence "This is a sample sentence." and you want just the word "sample". The MID function lets you isolate that word precisely. It does this using three key pieces of information:
- The Text: This is the entire string of text (e.g., "This is a sample sentence.").
- The Starting Point (
start_num): This is the position of the first character you want to extract (in our example, the 's' in "sample" is the 11th character, sostart_numwould be 11). - The Length (
num_chars): This is how many characters you want to extract after the starting point (the word "sample" has 6 letters, sonum_charswould be 6).
The function's syntax is simple: =MID(text, start_num, num_chars). Let's use our example sentence in cell A1: =MID(A1, 11, 6) would return "sample".
Real-World Examples: Putting the MID Function to Work
The MID function's applications are vast. Here are some practical examples:
Extracting Initials: If cell B1 contains "John Doe",
=MID(B1,1,1)&MID(B1,FIND(" ",B1)+1,1)extracts the initials "J.D." This usesFINDto locate the space and then extracts the first character before and after it.Working with Product Codes: A product code "XYZ-123-ABC" can be easily parsed.
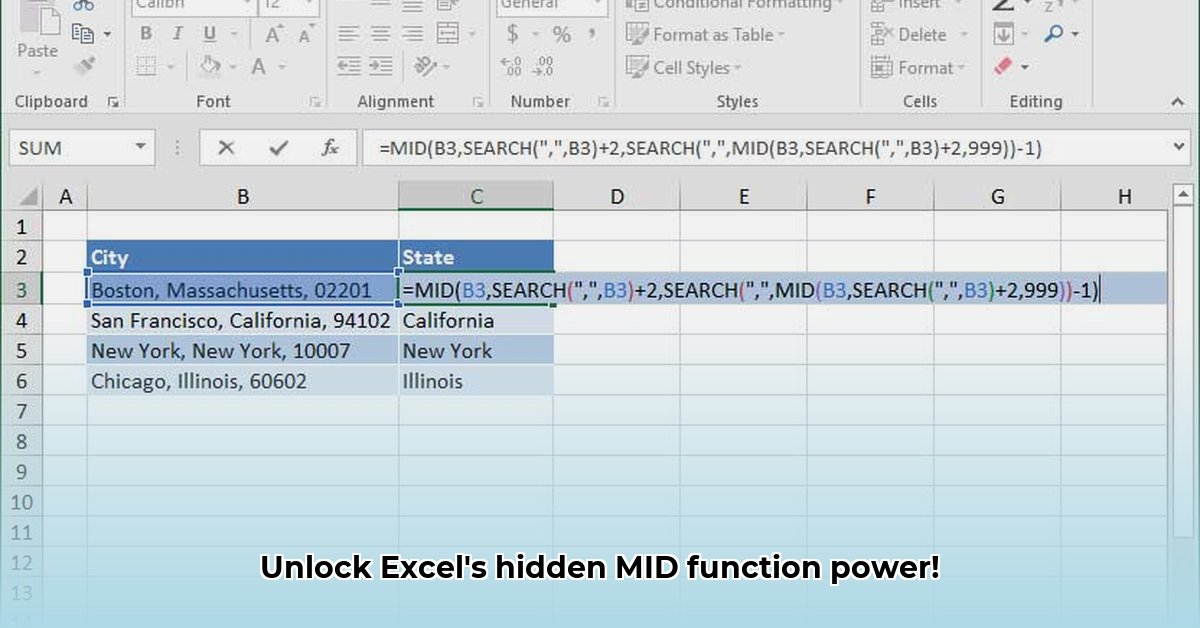
=MID(A2,1,3)extracts "XYZ",=MID(A2,5,3)gets "123", and=MID(A2,9,3)extracts "ABC". Efficient and precise!Data Cleaning: Imagine a column of addresses with inconsistent formatting. MID, combined with other functions, can standardize your data, making it easier to analyze. For example, you could extract zip codes or city names reliably.
Troubleshooting: Common Errors and How to Avoid Them
Even experts encounter problems! Here's how to handle common issues:
#VALUE!Error: This usually appears ifstart_numornum_charsaren't numbers. Double-check your inputs!Empty Cell ("") Result: This happens when your
start_numis larger than the length of the text string. Ensure your starting point is within the text's boundaries.
Remember: Accurate inputs are crucial for reliable results.
Taking it Further: Advanced Techniques and Combinations
To enhance your MID function skills, combine it with other powerful Excel functions:
LEFTandRIGHT: These extract text from the beginning and end of a string, respectively. Using them alongside MID provides complete control over text extraction.LEN: This function gives you the length of a string, which is vital for calculatingnum_charsdynamically. This makes your formulas more adaptable to different text lengths.FINDandSEARCH: These find specific text within a string, making locating your extraction point automatic.
Array Formulas: Processing Multiple Cells Simultaneously
Want to boost your efficiency? Array formulas apply MID to multiple cells at once! This significantly speeds up processing large datasets. For example, if A1:A10 contains names, {=MID(A1:A10,1,3)} (entered with Ctrl+Shift+Enter) returns the first three characters of each name.
Mastering the Art of Text Extraction
The MID function is invaluable for data manipulation. By understanding its arguments, common errors, and advanced applications, you'll significantly improve your Excel proficiency. Combine it with other functions for powerful text processing capabilities, and use array formulas for large-scale data manipulation. Mastering the MID function will transform your Excel workflow. Don't hesitate to experiment and discover its full potential!